Hands-on Knowledge: Navigating Hand and Thumb Arthritis

Over 100 distinct types of joint illnesses are together referred to by the general name “arthritis,” which is the most common cause of disability globally. Millions of people suffer from thumb and hand arthritis, mostly affecting complex hand joints. Examine these disorders’ causes, signs, and diagnoses and learn vital information that patients and medical professionals should be aware of.
Causes of Hand Arthritis and Thumb Arthritis
Arthritis in the hands and thumbs is usually caused by combined lifestyle, environmental, and hereditary factors. One major factor is the deterioration of joint cartilage over time. A family history of arthritis may also make someone more susceptible. Workplace dangers, including hard work or repetitive hand motions, could also be crucial. In addition, rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases can damage the joints, resulting in arthritis in the hands and thumbs.
Symptoms of Hand Arthritis and Thumb Arthritis
The symptoms of hand arthritis and thumb arthritis are straightforward but can be debilitating. People may feel pain, stiffness, and oedema in the afflicted joints. As grip strength decreases, simple chores become difficult. Deformities can also arise and change how the thumb and fingers line. These symptoms frequently worsen over time, impairing daily tasks and lowering hand function in general.
Diagnosis of Hand Arthritis and Thumb Arthritis
A diagnosis is essential for hand and thumb arthritis to be managed. Medical practitioners use imaging techniques, clinical evaluation, and medical history assessment to confirm the disease. X-rays can assess the degree of arthritis and show joint deterioration. Meanwhile, blood tests may be used to find inflammatory markers linked to certain kinds of arthritis, helping with differential diagnosis.
Clinical Evaluation
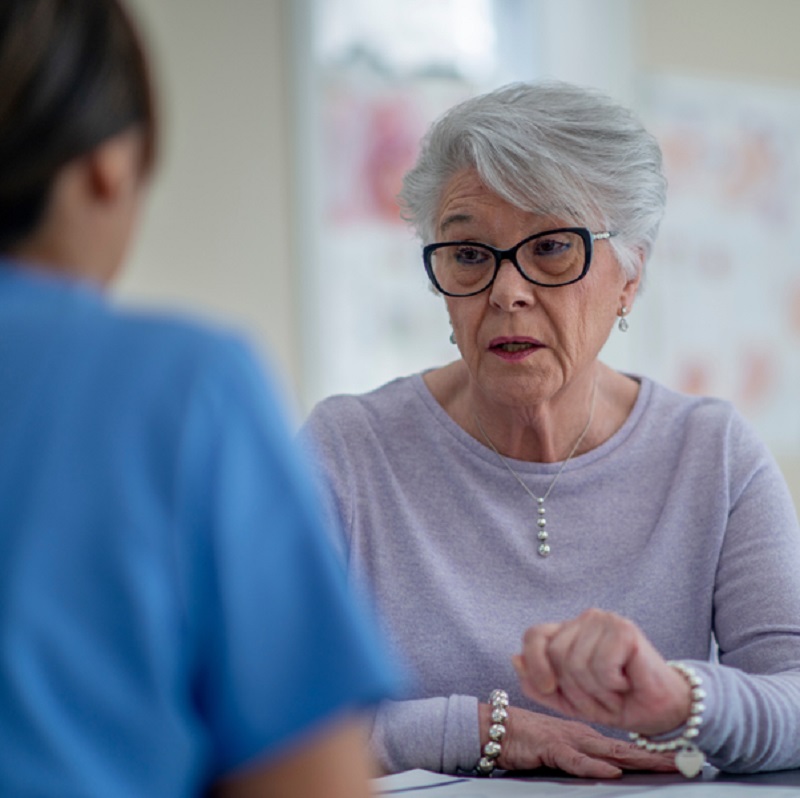
Healthcare professionals check the hands and thumbs for swelling, soreness, and range of motion during a clinical evaluation. They measure the patient’s grip strength and ask about their level of pain and functional limitations. This data is used with imaging and lab results to provide a picture of the patient’s condition that helps determine the course of action.
Medical History Assessment

Knowing the patient’s medical history is essential to diagnose hand and thumb arthritis. Inquiries about work-related exposures, family history, and the onset and course of symptoms enable medical practitioners to customise their care. Patients are urged to supply precise and complete information to aid with the diagnosis.
Imaging Studies
The most used imaging technique for identifying hand and thumb arthritis is X-rays. They contribute to the classification and severity assessment of the ailment by revealing bone spurs, cartilage loss, and joint injury. In certain situations, soft tissue visualisation using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be utilised to provide an understanding of the degree of joint involvement.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are also needed in diagnosing arthritis in the hands and thumbs. An inflammatory condition may be indicated by elevated levels of particular markers, such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP). Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies and rheumatoid factor are markers for rheumatoid arthritis that help distinguish it from other types of arthritis.
Differential Diagnosis
The symptoms of hand and thumb arthritis can be similar to those of other disorders, so a differential diagnosis is required. Arthritis symptoms might be mistaken for other conditions, such as bursitis, tendinitis, or carpal tunnel syndrome. A differential diagnosis guarantees the implementation of suitable therapies, preventing unnecessary treatments or postponements in resolving the underlying problem.
Conclusion
The crippling illnesses known as hand and thumb arthritis have a profound effect on the lives of those who suffer from them. Patients and healthcare providers should comprehend the causes, symptoms, and diagnosis to manage it. For patients suffering from these disorders, a proactive approach to diagnosis and treatment can help reduce symptoms, help regain functionality, and lessen these illnesses’ influence on everyday activities, enriching their quality of life.
Reclaim your freedom from hand and thumb arthritis. Visit the Advanced Hand Centre to learn more.